How to connect via ssh to windows
Connect to Windows via SSH like in Linux
The most depressing thing for me is to connect to Windows hosts. I’m not an opponent or a fan of Microsoft and their’s products. Every product has its own purpose. But it is really painful for me to connect to Windows servers, because of 2 points: it is hard to configure (Hi WinRM with HTTPS), and it is really unstable (Hello RDP to VMs across the ocean).
Fortunately, I found the project Win32-OpenSSH. I realized that I want to share my experience with it. I believe it will help somebody and save a lot of nerves.
Installation ways:
I must note, this project is on beta stage and it isn’t recommended to use it in production.
Well, let’s download latest release. Currently it is 7.9.0.0p1-beta. It also has 32 and 64 bit versions.
Then unpack it to C:\Program Files\OpenSSH.
Important: It is necessary to grant write access to SYSTEM and Administers group only.
Futher, install services via shell script install-sshd.ps1 which is located in the OpenSSH directory
Let’s allow incoming connections on 22 port:
Note: applet New-NetFirewallRule is for Windows Server 2012 and above only. For older or desktop OS, you can use the following command:
This will automatically generate host keys under %programdata%\ssh if they don’t already exist.
You can set up the service auto-start by command:
Also, you can change default shell (it is cmd by default after install):
Note: you must define absolut path.
We can configure sshd_config, which is located in C:\ProgramData\ssh.
E.g.:
Then we create .ssh directory inside the user directory (C:\Users\ ) and authorized_keys file inside it. We can paste public keys into this file.
Important: the only user in which directory it is, must have write permissions for this file.
By the way, if you can’t fix it, you can disable permissions check via config:
Also, directory C:\Program Files\OpenSSH contains 2 scripts (FixHostFilePermissions.ps1, FixUserFilePermissions.ps1), which should but not obliged fix permissions, including authorized_keys permissions, but they don’t.
Don’t forget to restart sshd service to apply changes.
Как подключиться к серверу по SSH?
SSH-протокол (англ. Secure Shell ) используется для безопасного удалённого управления операционной системой. По SSH можно подключиться к любому серверу с операционной системой семейства Linux.
Если на вашем сервере установлена ОС Windows Server — используйте подключение по RDP.
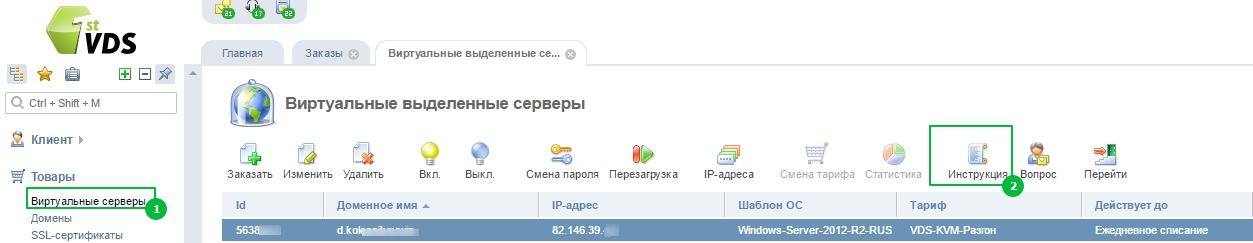
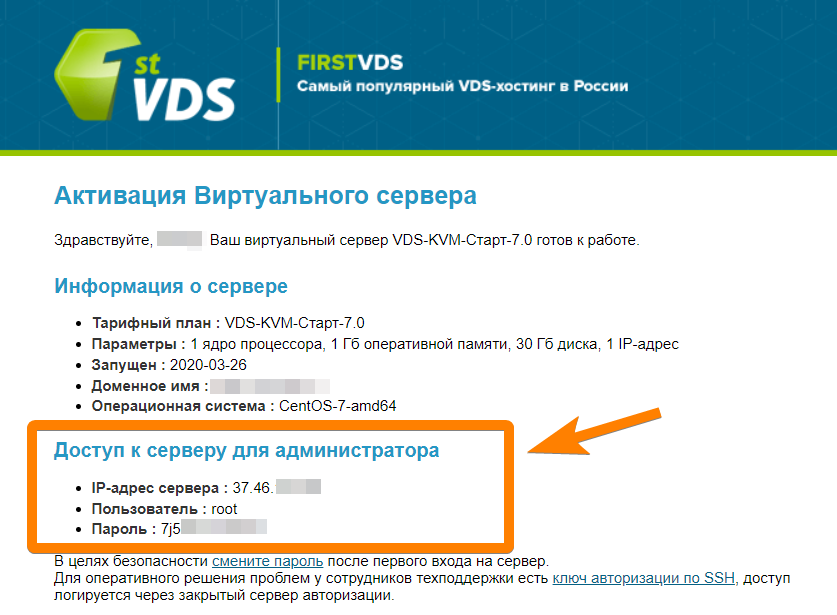
Где найти доступы к серверу
В новой вкладке откроется страница с необходимой информацией.
Как подключиться по SSH с компьютера на ОС Windows
Если на вашем компьютере установлена ОС Windows, а на сервере — UNIX-подобная система (например, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS и др.), то для установки SSH-соединения можно использовать PuTTY. Это бесплатная программа под Windows состоит из одного запускаемого файла и не требует установки.
Чтобы установить соединение при помощи PuTTY, необходимо проделать следующие действия:
0. Скачайте нужную версию PuTTY по ссылке
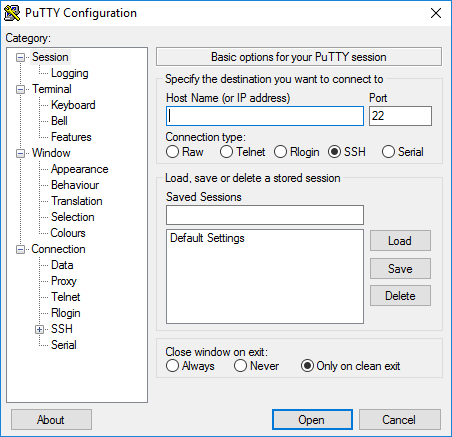
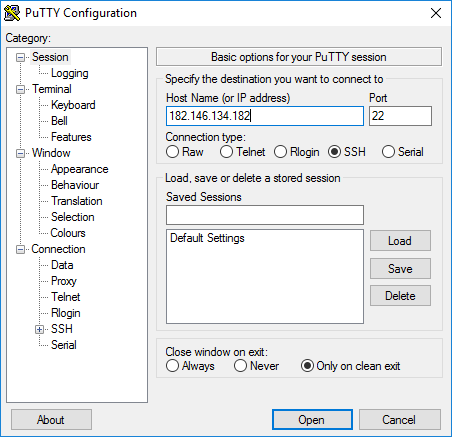
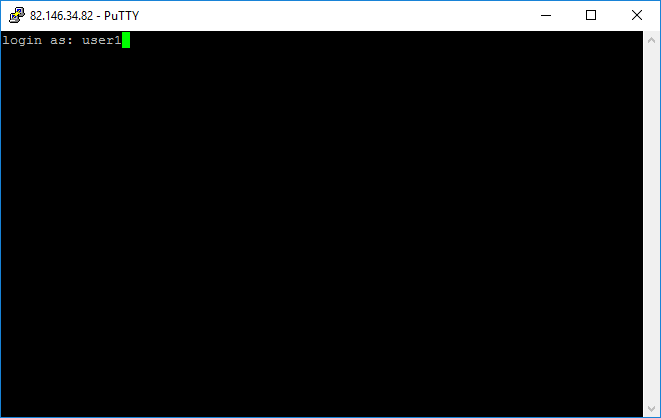
1. Запустите файл putty.exe. Откроется окно программы:
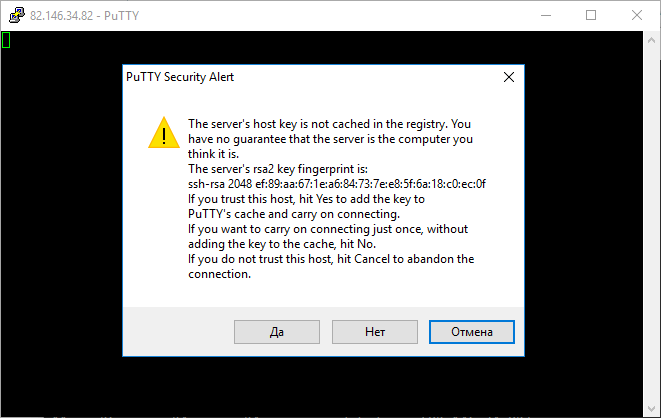
По умолчанию никаких настроек программы менять не нужно. Достаточно убедиться, что указан порт Port 22 и тип соединения Connection type — SSH.
Может появиться предупреждение системы безопасности PuTTY — оно срабатывает при подключении к новому серверу. Нажмите Да — и соединение продолжится.
Как подключиться к серверу по SSH с компьютера на Linux/MacOS
Подключиться по SSH к виртуальному серверу можно через терминал — в обоих случаях это приложение предустановлено.
В MacOS приложение Терминал можно найти через Spotlight (иконка поиска в правом верхнем углу экрана).
Подключиться к виртуальному серверу по SSH можно одной командой:
где вместо username нужно указать логин пользователя, вместо ip-adress — IP-адрес сервера, к которому вы подключаетесь. Если на сервере используется нестандартный порт SSH, команда изменится:
где 22 — порт, по которому будет произведено подключение по SSH.
После ввода команды система запросит подтверждение подключения (необходимо ввести yes и нажать Enter ) и пароль пользователя. После ввода нажмите клавишу Enter — откроется SSH-соединение:
How to connect to the server via SSH (Linux, Windows and Mac)?
To connect and manage your server, you can use WHM/cPanel, however, it is often not possible to do everything from the graphical interface, so you should look for SSH connection support.
Adriahost has VPS and Dedicated servers, Linux and Windows servers in its offer. On all these services, customers get complete Root access and all the options that are needed to improve the online business.
What is SSH (Secure Shell)?
Secure Shell is an encrypted network protocol for managing network systems in a secure way using an insecure network (the Internet). SSH allows users to connect to a computer-server via a secure connection. In this way, all data is encrypted so that it becomes illegible to people who should not have access to this data.
The specific purpose of this kind of connection is to provide you a quick and secure way to perform a specific task on your server. For example, you can restart a particular service or a complete server if no other way delivers results.
SSH connection to the server
A computer with a Windows operating system
To connect to your server using the Windows operating system, first download the PuTTY executable file from here:
After downloading the file, you do not need to install it, it is enough to start it (click twice on file). A window will open where you need to enter the server’s IP address, port and click on the Open button to connect:
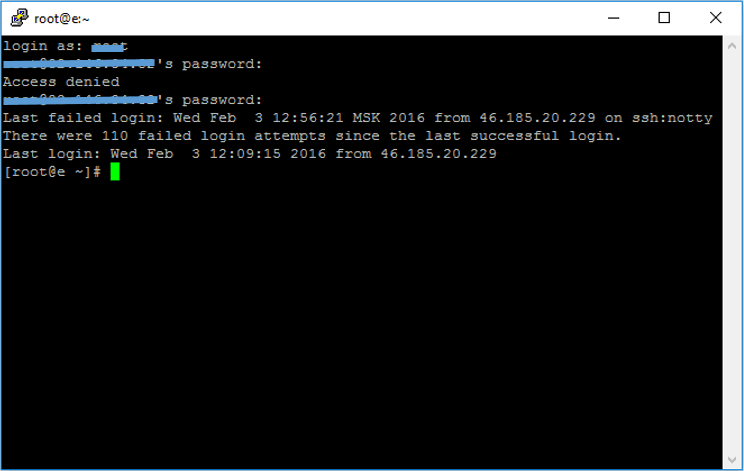
A command terminal will open where you need to enter the username and password information. If you want to log in as root (ultimate privileges), type root for Login as and press Enter. The next thing you need to enter is the password, so note that if you copy the password, you can do the paste by just clicking with the right-click in the inside of the terminal.
Please note that password entry is not visible and no password or symbols will appear for it. After entering the password, press Enter.
For computers running Linux and Apple Mac operating systems
You can use Open SSH on Linux and Apple Mac computers. Just open the Terminal and type the following:
Replace the username with the user name you are accessing with, while the hostname.domain.ext or ipaddress replace with the hostname or IP address. If you access using root user, just enter root@hostname.your-website.com or root@91.201.129.561
If you are using the Ubuntu operating system, you can install Open SSH using the following command:
For Apple Mac users, SSH comes by default, but SSH Deamon is turned off. You need to activate it using the following command:
To stop the SSH Daemon, you need to type the following:
To check SSH status, use the following:
Carefully with the SSH data and actions you want to apply
It is important to keep safe all your data for accessing your server. Do not allow your data to come into the possession of people who do not have a need to access and who can by accident or intentionally endanger your work. When you access the server via SSH connection you will see that everything is going fast and effective. With one command you can restart the server or a specific process so be very careful and plan well each action before you press Enter.
You can see the complete offer of our servers on the following pages: VPS servers, Dedicated servers, VPS and Dedicated Windows servers.
You can send us any questions using our contact form or directly from your client account.
How To Use SSH to Connect to a Remote Server
Last Validated on November 11, 2020 Originally Published on September 10, 2013
Introduction
One essential tool to master as a system administrator is SSH.
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a protocol used to securely log onto remote systems. It is the most common way to access remote Linux servers.
In this guide, we will discuss how to use SSH to connect to a remote system.
Basic Syntax
To connect to a remote system using SSH, we’ll use the ssh command. The most basic form of the command is:
The remote_host in this example is the IP address or domain name that you are trying to connect to.
This command assumes that your username on the remote system is the same as your username on your local system.
If your username is different on the remote system, you can specify it by using this syntax:
Once you have connected to the server, you may be asked to verify your identity by providing a password. Later, we will cover how to generate keys to use instead of passwords.
To exit the ssh session and return back into your local shell session, type:
How Does SSH Work?
In the previous section, ssh was the client program. The ssh server is already running on the remote_host that we specified.
On your server, the sshd server should already be running. If this is not the case, you may need to access your server through a web-based console, or local serial console.
The process needed to start an ssh server depends on the distribution of Linux that you are using.
On Ubuntu, you can start the ssh server by typing:
That should start the sshd server and you can then log in remotely.
How To Configure SSH
When you change the configuration of SSH, you are changing the settings of the sshd server.
Back up the current version of this file before editing:
Open it with a text editor:
You will want to leave most of the options in this file alone. However, there are a few you may want to take a look at:
The host keys declarations specify where to look for global host keys. We will discuss what a host key is later.
These two items indicate the level of logging that should occur.
If you are having difficulties with SSH, increasing the amount of logging may be a good way to discover what the issue is.
These parameters specify some of the login information.
LoginGraceTime specifies how many seconds to keep the connection alive without successfully logging in.
It may be a good idea to set this time just a little bit higher than the amount of time it takes you to log in normally.
PermitRootLogin selects whether the root user is allowed to log in.
In most cases, this should be changed to no when you have created a user account that has access to elevated privileges (through su or sudo ) and can log in through ssh.
strictModes is a safety guard that will refuse a login attempt if the authentication files are readable by everyone.
This prevents login attempts when the configuration files are not secure.
These parameters configure an ability called X11 Forwarding. This allows you to view a remote system’s graphical user interface (GUI) on the local system.
You should thoroughly test your changes to ensure that they operate in the way you expect.
It may be a good idea to have a few sessions active when you are making changes. This will allow you to revert the configuration if necessary.
How To Log Into SSH with Keys
While it is helpful to be able to log in to a remote system using passwords, it’s a much better idea to set up key-based authentication.
How Does Key-based Authentication Work?
Key-based authentication works by creating a pair of keys: a private key and a public key.
The private key is located on the client machine and is secured and kept secret.
The public key can be given to anyone or placed on any server you wish to access.
When you attempt to connect using a key-pair, the server will use the public key to create a message for the client computer that can only be read with the private key.
The client computer then sends the appropriate response back to the server and the server will know that the client is legitimate.
This entire process is done automatically after you set up keys.
How To Create SSH Keys
SSH keys should be generated on the computer you wish to log in from. This is usually your local machine.
Enter the following into the command line:
Press enter to accept the defaults. Your keys will be created at
Look at the permissions of the files:
As you can see, the id_rsa file is readable and writable only to the owner. This is how it should be to keep it secret.
The id_rsa.pub file, however, can be shared and has permissions appropriate for this activity.
How To Transfer Your Public Key to the Server
If you currently have password-based access to a server, you can copy your public key to it by issuing this command:
This will start an SSH session. After you enter your password, it will copy your public key to the server’s authorized keys file, which will allow you to log in without the password next time.
Client-Side Options
There are a number of optional flags that you can select when connecting through SSH.
Some of these may be necessary to match the settings in the remote host’s sshd configuration.
For instance, if you changed the port number in your sshd configuration, you will need to match that port on the client-side by typing:
If you only wish to execute a single command on a remote system, you can specify it after the host like so:
You will connect to the remote machine, authenticate, and the command will be executed.
As we said before, if X11 forwarding is enabled on both computers, you can access that functionality by typing:
Providing you have the appropriate tools on your computer, GUI programs that you use on the remote system will now open their window on your local system.
Disabling Password Authentication
If you have created SSH keys, you can enhance your server’s security by disabling password-only authentication. Apart from the console, the only way to log into your server will be through the private key that pairs with the public key you have installed on the server.
Warning: Before you proceed with this step, be sure you have installed a public key to your server. Otherwise, you will be locked out!
As root or user with sudo privileges, open the sshd configuration file:
After making your changes, save and close the file.
You can now reload the SSH daemon:
Password authentication should now be disabled, and your server should be accessible only through SSH key authentication.
Conclusion
Learning your way around SSH is a worthwhile pursuit, if only because it is such a common activity.
As you use the various options, you will discover more advanced functionality that can make your life easier. SSH has remained popular because it is secure, light-weight, and useful in diverse situations.
The Developer’s Guide to Start Using SSH (Connect to Your Server Securely)
Learning how to use SSH to access your WordPress site is something you may not have considered. For most WordPress users, the most familiar way to connect to your site will be via the WordPress dashboard and admin screens, combined with SFTP and phpMyAdmin to access the database.
But SSH might just prove to be one of the most valuable tools in your WordPress toolbelt.
If you want to speed up your workflow, you’ll find that learning how to use SSH to connect to your WordPress site will make you more efficient.
In this post, we’ll show you how to do it.
What is SSH?
First, let’s start by identifying what SSH is and when you might use it.
SSH means ‘Secure Shell’. The SSH specs define it as:
“A protocol for secure remote login and other secure network services over an insecure network.”
This means you can use it to access your WordPress site remotely, from any computer and regardless of where your site is hosted, as long as you have the login credentials. Using this method is inherently secure.
SSH is designed to provide secure login, so you can be confident no one can access your connection while you are using it. It’s also quick and easy to use once you’ve got the hang of it. And if you want to interact with the WordPress REST API, it’s one way to send commands.
To connect to your server via SSH, you’ll need two things:
If you’re running Linux or macOS, you have an interface built into your operating system, so you don’t need to install an SSH client. But if you’re running Windows, you’ll need to install a client. I’ll show you how to do that in this post.
Tools You Need to Connect to Your Site via SSH
To start, you’ll need to use either the terminal or an SSH client. These work in very similar ways.
Connecting via the Terminal on macOS or Linux
The Terminal is an application that comes with Linux or macOS, that allows you to use the command line to send commands, either to your machine or to a remote server.
It isn’t a graphical interface so you won’t be using a mouse. Instead, you type in text commands. For a first-time user, it can be little disconcerting, as you’re probably used to seeing visual representations of your commands. But once you get used to it, you’ll find it quicker.
If you worked with computers in the days before graphical user interfaces, using systems such as Microsoft’s MS-DOS, you might be familiar with this kind of interface. The good news is that the Terminal gives you many more options than MS-DOS did!
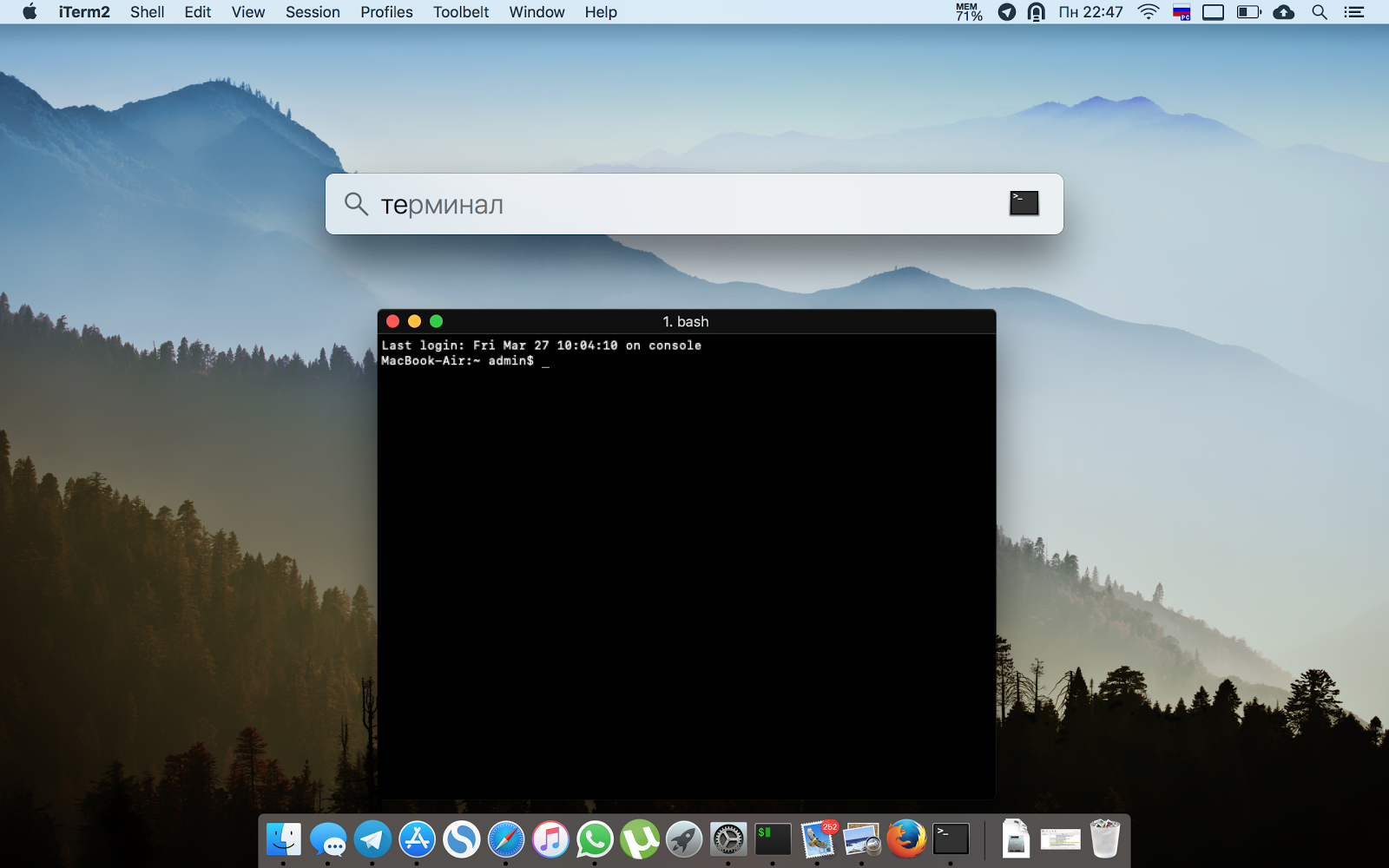
To open the Terminal on Mac, open Spotlight and type Terminal. You can also access it via Applications > Utilities.
Finding Terminal on Mac
To open Terminal on Linux, find it in the Applications menu. If it isn’t immediately obvious, type Terminal into the prompt to find it.
Connecting via an SSH Client on Windows
An SSH client is a program that you’ll need to install if you’re running Windows, in order to connect via SSH.
The most popular SSH client is PuTTY. You’ll need to download and install that before you can access your site from Windows.
Installing the Putty SSH Client on Windows
Start by going to the PuTTY download page.
The PuTTY download page
From here, choose the package that corresponds to your version of Windows. If you aren’t sure whether to download the 32-bit or 64-bit version, check out the FAQ page. If in doubt, the 32-bit version is the safer option.
Click on one of the two options under MSI (‘Windows Installer’). The file will download to your machine and run the installer.
Once PuTTY has installed, open it and you can then use it to connect to your site.
How to Connect to Your Server via the Command Line
Once you’ve found or installed the Terminal or an SSH client, the next step is to connect to your remote site.
In either Terminal or an SSH client, you use the command line to connect and send commands to your server. That’s the terminology I’ll use from now on, instead of referring to Terminal or an SSH client.
To do this, you’ll need four pieces of information:
The server address is usually your domain name or IP address. If your site is hosted with Kinsta, use your IP address.
The username and password will be your FTP username and password, not the ones for your WordPress admin.
The port will be provided by your hosting provider. In some cases, a default port is used, but for extra security at Kinsta, we use different ports for different sites.
In MyKinsta, you can find the details by selecting your site and finding the SFTP/SSH section of the Info screen.
Just copy this and paste it into the command line.
Once you’ve done that, you will be prompted for your password. Copy that from MyKinsta and you’ll be given access to your server.
You’ll see a screen that looks something like this:
Kinsta SSH starting screen
If you’re not with Kinsta hosting, your screen will look a little different, but will still give you access to your server.
How to Use SSH to Interact with Your Site
Now you can start using SSH to interact with your server and your site. There are a number of SSH commands you can use as well as the commands provided by the WordPress Command Line Interface (WP-CLI).
SSH is a very powerful tool and if you aren’t careful, you could break your site. It will let you add and delete files, so if you enter the wrong command, you could lose content or delete all your images, for example. Always use it with caution and make sure you backup your site before using it.
Basic SSH Commands
SSH comes with a range of commands you can use to connect and interact with your server.
Once you’ve looked into your server via the command line, you simply type in SSH commands in the same way you would do if you were using Terminal to interact with your own computer.
Let’s take a look at some of the most useful SSH commands you could start using.
The ls Command
Use the ls command to get a list of the files and directories in your current location. You can add more to the command to get more information:
The cd Command
Use the cd command to change directories. You’ll be taken to the new directory and the command line will indicate where you are:
You can then use ls again to find out what’s in the new directory.
Sign Up For the Newsletter
We grew our traffic 1,187% with WordPress. We’ll show you how.
Join 20,000+ others who get our weekly newsletter with insider WordPress tips!
You can use cd to move down more than one directory or to move up or across directories. To go up, enter two dots after cd like this:
And to go to a specific directory, type the full directory path such as:
The mkdir Command
Use the mkdir command to create a new directory. So if I’m in the themes directory, I could create a new directory for a new theme:
The touch Command
Once I’ve created my new directory, I could add a new file to it using the touch command:
The cat Command
To display the contents of a file, use the cat command.
The rm Command
Use the rm command to remove a file or folder. Use with caution, as this can’t be undone:
The cp Command
The cp command is used to copy files and folders. You need to provide the name of the file or folder and the location where you want to copy it.
You can also add options at the beginning of the command, but don’t need to. So to copy the footer.php file from one theme to another when you’re in the wp-content directory, you would use this:
Don’t add a name for the destination file. If you do, and there’s already a file with that name at that destination, then the file will be overwritten with the contents of the file you’re copying.
Need a blazing-fast, secure, and developer-friendly hosting? Kinsta is built with WordPress developers in mind and provides plenty of tools through a powerful dashboard. Check out our plans
If you don’t include a filename in the detonation and that file already exists, then you will get an error message and the copy won’t take place.
I’ve already mentioned that there are some optional elements you can add at the beginning of this command. These are:
The mv Command
As an alternative to copying a file, you can move it using the mv command. For this, you just provide the source and destination: there are no options.
This will remove the footer.php file from theme1 and move it to theme2. If you do this with a folder, it will always move the files and folders within that directory too.
You can find information about more SSH commands in the SSH documentation.
Using WP-CLI to Interact with Your Site
In addition to the standard SSH commands, WordPress also gives you the WP-CLI interface, which provides even more commands. This includes interacting with files and folders, the admin options, and your database.
With Kinsta, WP-CLI comes with your hosting and you can start using it straight away. If your hosting provider doesn’t give your WP-CLI, you can install it by following the steps in this guide to WP-CLI.
Testing and Troubleshooting Your SSH Connection
Sometimes you might find that SSH doesn’t behave in the way you want it to. Either you can’t connect, or the command you’ve used doesn’t work in the way you expect.
If that happens, try some of these troubleshooting tips.
If You Can’t Connect Through SSH
If you can’t connect to your server, take a look at any error messages or prompts that the command line gives you. Sometimes you’ll have to reply to a yes/no prompt or fix a typo in your command.
If that doesn’t work, check that the login credentials you provided are correct. You will be able to get these from the Info page for your site in MyKinsta. Other hosting providers will probably have an SSH section in cPanel or whichever dashboard they’re using.
If you’ve tried again and it still doesn’t work, try resetting your SSH password. Check that your internet connection is working and there isn’t a firewall preventing you from accessing your server. If in doubt, close Terminal or your SSH client down and open it up again.
Log in to your hosting account and check that there aren’t any server issues preventing you from gaining access. If you’re with Kinsta, go to our system status page to find out if anything isn’t working.
Kinsta system status screen
If you’re on a public network, it may not allow SSH access to your port. Try testing it with other ports that you know are working.
If all else fails, open a support ticket with your hosting provider who will be able to access logs and work out why you haven’t been able to connect.
If Your SSH Commands Don’t Work as They Should
Another common problem is for an SSH command not to work in the way you expect it to. This is normally due to the command being entered incorrectly.
Here’s an example where I typed is instead of ls :
Inputting a typo in Terminal
Here, I’m presented with an error warning ( command not found ) so I try again, with the correct command.
Sometimes you might type the command correctly but get the parameters wrong. If this is the case, check the SSH documentation for SSH commands and the WP-CLI documentation for WP-CLI commands.
If your SSH commands don’t work because the connection isn’t working, you will see an error message telling you this. The command line constantly provides you with information on what’s going on, which is one of its benefits. In fact, it often gives you more and clearer information that a graphical interface.
How to Generate a New SSH Key Pair for Extra Security
Generating an SSH key pair adds an extra layer of security when compared to using your username and password to connect to SSH. You do it from within the Terminal or your SSH client. Here’s how.
Generating a key pair involves three steps:
Adding SSH key in MyKinsta
You can find full instructions on doing this in our guide to generating SSH key pairs for macOS, Linux, and Windows.
Summary
Using SSH to connect to your server and your WordPress site will make you more efficient than relying on the WordPress admin interface, FTP, and even phpMyAdmin.
Follow the steps above to connect to your server via SSH and you’ll find you can do more on your site without having to switch between applications or browser windows.
Now it’s your turn: what’s your preferred terminal command you use on a daily basis? Let us know in the comments!
If you enjoyed this article, then you’ll love Kinsta’s WordPress hosting platform. Turbocharge your website and get 24/7 support from our veteran WordPress team. Our Google Cloud powered infrastructure focuses on auto-scaling, performance, and security. Let us show you the Kinsta difference! Check out our plans
Hand-picked related articles
How to Speed up Your WordPress Site
Speed is everything. Higher conversions, better rankings & SEO, more sales. Learn how to make your WordPress site blazing fast with this in-depth g.
10 Best FTP Clients for WordPress Users (Mac and Windows)
Finding the best FTP clients is important when it comes to managing and transferring files. We’ve done the work for you: pick the best FTP client now!
WP-CLI v2 – Managing WordPress From the Terminal
WP-CLI v2 is a powerful command line tool for developers to manage WordPress installations. Check out how to install and use WP-CLI commands.